The Internet of Things (IoT) has moved beyond Gartner’s hype cycle from being a mere buzzword to delivering anticipated benefits for enterprises, people and society. Going by the level of sophistication and adoption of IoT applications, Norton estimates that there will be more than 21 billion IoT devices worldwide by 2025, a two-fold increase compared to what we have now. Smart navigation, intelligent virtual assistants, high-tech appliances, cutting-edge security systems, and the list is endless. This ubiquitous computing that IoT has turned into a reality is visible around you from the time you wake up to logging out for the day.

What is the future of IoT Services?
The growth of IoT technology stems from a constant need to reduce human involvement with machines. From metals to the medical industry, from warehouses to homes, the tools and gadgets around us are being enabled to better understand how they are being used. This also allows enterprises to move to a predictive instead of a reactive mode, saving costs and increasing operational efficiency, among other benefits. Consider this: In a trial conducted at Port of Qingdao in China, it was found that up to 70 percent of labor costs can be saved with an IoT-enabled 5G automation upgrade compared to a traditional harbor. They found that IoT-enabled smart harbors with automated ship-to-shore (STS) cranes operated from a control center could lift containers over a 5G connection.
These are just a few examples of the advancements that IoT has made across different domains. IoT services enable greater automation, better user experience, seamless adaptability of devices, and reduced human interference in the overall workflow.
Here are some interesting use cases around IoT:
- Healthcare and IoT
The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of IoT Services. With Artificial Intelligence (AI) learning and monitoring and the development of Healthcare IoT (H-IoT) systems, opportunities for improved personalized healthcare with lower costs and eventually, better facilities for all have been made possible. According to research, the value of the healthcare IoT sector is expected to touch nearly $177 billion by 2026. Emerging IoT-based applications like non-invasive body-worn and implanted devices, actuators, intra-body networks of implants, and biomedical therapies in new healthcare applications can save and significantly improve the quality of life. Research is also being conducted on device and network co-design solutions. These are expected to integrate medical procedures with even more complex cyber capabilities using intra-body and extra-body communication systems based on IoT.

Coupled with IoT, these innovations have become useful not just for diagnostics and surgery, but also in data analysis for personalized human health monitoring, including intra-organ functions and ailments, biomedical therapy, remote surgery, and biometric authentication. Besides these, IoT has found use in post-operative care as well through practicing defined protocols. All this is being done through methods such as
- Fluidic diagnostic monitoring- This is a continuous and real-time monitoring of the characteristics and levels of various fluids in the body using IoT. Alerts are provided for any abnormalities in the fluid levels immediately, ensuring immediate treatment.
- Non-invasive sensors- These IoT-enabled sensors continuously monitor a patient’s condition remotely and in real-time. Non-invasive sensors include pulse oximeters, transcutaneous electrodes for Po2 and Pco2, and transcutaneous bilirubin monitors.
- Wearables (electronic health sensors) – Several wearable devices, such as smartwatches paired with smartphones, can allow for personalized monitoring of a person’s condition. These IoT-powered devices can monitor heartbeat, body temperature, blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and oxygen levels in the body.
- Implanted health sensors- Using IoT data, these sensors enable in-situ monitoring of the physiological conditions of a patient. IoT has proven especially useful for such devices. This is because the sensed measurements, including drug volumes and actuating directives, need to be communicated to an external monitoring station and body devices embedded elsewhere. For example, it could be on the body’s surface or even as implants in other parts of the body. One of them or a combination of these IoT-based methods has revolutionized healthcare. These personalized, reliable, and secure solutions can detect health risks from diseases. Some conditions for which IoT technologies are being used include cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, oncological issues, kidney diseases, and Parkinson’s disease.

Eldercare has for long been an understudied and logistically difficult field of medicine. This is because of the requirements for continuous human intervention. But with the IoT, caring for the elderly can now be managed better. IoT-based tools like Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) and intelligent devices can remove the need for continuous human presence with the elders. Telemedicine and smart wearables devices have also made better care available for them. These also use AI to track daily routines, monitor health parameters and notify healthcare authorities should problems arise.
- Future of the workplace and IoT
Restrictions are easing now as the pandemic abates, but the hybrid working norm means companies will continue to use technologies and professional automation tools to get work done remotely. These include video conferencing tools, advanced analytics, data monitoring, work processes, and schedules. All these will help to create a collective intelligence that increases efficiency. Even traditional manufacturing companies that require a physical presence will use IoT data to monitor factory floor processes remotely.
IoT connectivity also addresses time-critical communication needs across various industries, enabling innovative services for consumers and enterprises. Time-critical needs include processes requiring the delivery of data and information within specified time duration and certain specific reliability levels.
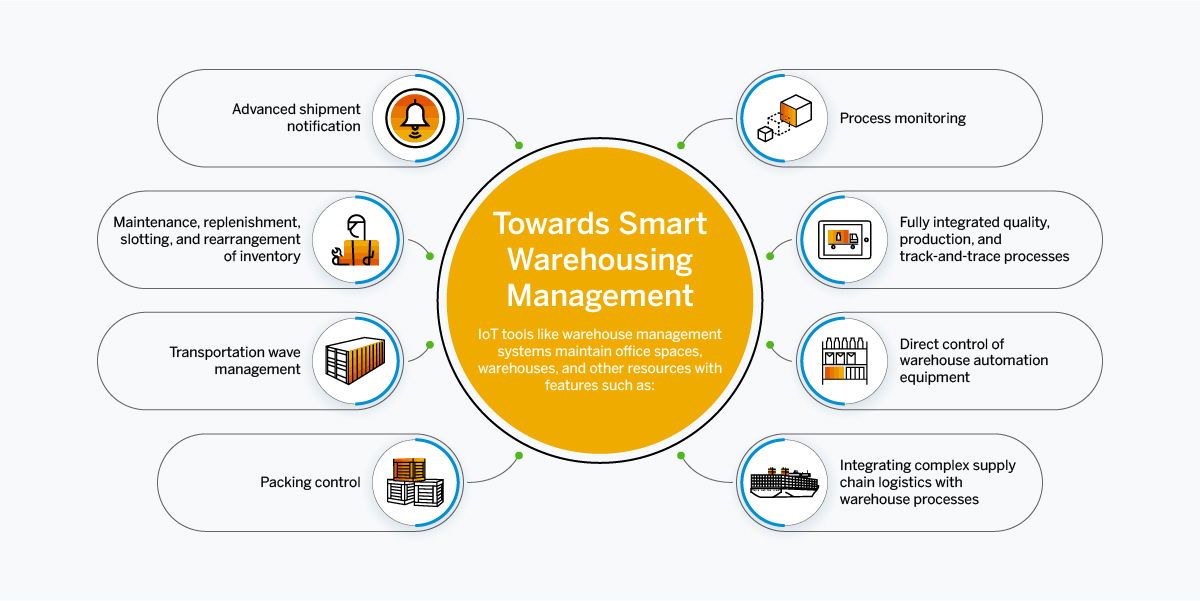
Maintaining office spaces, warehouses, and other resources can also be done with the help of IoT tools like
- Advanced shipment notification
- Maintenance, replenishment, slotting, and rearrangement of inventory
- Transportation wave management
- Packing control
- Process monitoring
IoT allows managing high-volume warehouse operations through applications such as on-premise and cloud deployment, fully integrated quality, production, and track-and-trace processes and direct control of warehouse automation equipment. By integrating complex supply chain logistics with warehouse and distribution processes, IoT Services allows for remote management of workplaces.
Working from home has also been made easier with the home automation systems based on IoT solutions like sensors, microcontrollers, and LAN or wireless communications. They help stay in touch with the workplace while making homes more enjoyable to live in.
Home automation systems based on IoT can also be used to command or control devices. Wireless technologies, predictive engines, and Natural Language Processing (NLP) have made it possible to control the home environment from a smartphone, allowing an unhindered work from home experience. These applications can monitor doors, home appliances, and bed movements, making homes more secure and responsive.
- Retail and IoT
The retail sector has also seen widespread adoption of IoT Services. Since the opening of the first IoT-enabled store in Sweden in 2016, many unstaffed retail shops have mushroomed. E-Commerce giants such as Alibaba and Amazon have launched interesting initiatives with IoT at the center of delivering new customer experiences. The new formats of retail stores are fully automated supermarkets and are also based on IoT applications. These include the use of Radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags and remote monitoring systems. Other IoT features, such as predictive engine, recognition, and Single-Shot Detector (SSD) algorithm, enhance the efficiency of automated retail systems. This has greatly increased the customer flow and transaction volume. One of the ways these will help retail outlets is by enabling decisions concerning stock placement and replenishment based on customer interaction with products displayed on the store shelves. The trend is catching on, and it’s just a matter of time before we see a completely human intervention-free retail world!
Besides all this, IoT can help the retail sector by providing additional capabilities in data auto-capture, visibility, intelligence, and information sharing. Besides enabling better customer servicing and greater integration of retail supply chains, other ways that IoT enhances the retail sector include-
- Monitoring supply chain networks
- Helping to maintain records of stocks and inventories
- Tracking shipments
- Pre-empting adverse conditions
- Managing yard logistics and warehouses
The pandemic has highlighted the intrinsic risks in modern supply chains, and for businesses, it makes maintaining efficient and cost-effective systems even more critical. In such a world, IoT data and IoT services can help businesses through improved supply chain efficiency implemented by using better managerial decision-making processes. These include multi-objective optimization of supply chain networks, partner selection in green supply chain problems, multi-product supply chain networks, and the problem-solving approach to closed-loop supply chains.
These can enhance supply chain performance in every dimension, including cost, quality, delivery, or flexibility. IoT can help the retail sector improve and maintain strong financial, social, and environmental sustainability.
- Cybersecurity and IoT
With the growth of IoT, there is an increasing threat of cyberattacks. Consequently, cybersecurity has become one of the most important areas of the Internet of Things. The IoT security market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 33.7% by 2023.
IoT cybersecurity serves to reduce cybersecurity risk for organizations and users through the protection of connected assets and data privacy. A robust IoT data security portfolio extensively uses advanced cryptography techniques to protect users from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks and other vulnerabilities. It also pre-empts any threats and takes measures to eliminate them before things get out of hand. The IoT aspects such as machine learning and physical unclonable functions also allow for preventing, detecting and reporting threats related to different domains of the IoT systems. These help in identifying authentic devices and preventing tampering and the insertion of cloned devices in the IoT environment. IoT is now also being used to maintain and protect public services in smart cities, and IoT cybersecurity has an important part to play.
As IoT utilization increases, other technologies and innovations that could keep up with it like 5G, blockchain, and AI have only now started to emerge. Using various machine learning algorithms, the enormous amounts of data that IoT can process and convert into relevant information can enhance efficiency and reduce costs. IoT data on various operational aspects are highly useful for organizations. Other fields such as agriculture and construction can also benefit from the tools available with IoT. And there’s no denying that IoT is fast becoming one of the most essential technologies for humankind. As we enter the new normal, IoT will playing an even more prominent role in every part of our lives.
Humans will have a pivotal role in the next phase of IoT services, where Industry 4.0 (Industrial Internet of Things) and Human 4.0 converge. Smart manufacturing is leading the way. As connected manufacturing optimizes itself automatically, it becomes increasingly economical to build and customize products while enhancing system efficiencies without human intervention. SAP manufacturing solutions are enabling pioneers to walk this path and set the agenda for the next frontier, where ‘humans’ and ‘machines’ speak the same language.



