MSMEs are the backbone of the Indian economy. With more than 6.3 crore micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) contributing nearly 29% to the country’s GDP, there is an immense scope to scale up this segment.

A key driver to this anticipated growth is the Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan which aims at creating a self-sufficient India. The program is built on five major pillars:
- ‘Economy,’ which drives quantum change rather than incremental change
- ‘Infrastructure’ and
- ‘System’ which is based on 21st-century technology-driven arrangements;
- ‘Democracy,’ which is the source of energy for a self-sufficient India; and
- ‘Demand,’ in which the strength of our supply chain is fully utilized.
MSMEs in India play an important role in reducing regional imbalances. They ensure a more equitable distribution of national income and wealth by offering substantial job opportunities at a lower capital cost than major businesses. MSMEs are known to contribute to the industrialization of rural and backward areas.
The Missing Middle and Challenges in Scaling Up
Unlike other economies though, the Indian MSME segment finds it harder to scale up. What economists call ‘the missing middle’ has become a perpetual puzzle difficult to solve. Whether in the manufacturing sector or other verticals, the ‘missing middle’ is ever-present. A natural progression is for enterprises to be micro-sized, grow to small entities and scale up to become mid-sized and later large companies. In India, a peculiar situation arises. Companies start small, stay small and fail to scale up. This is the ‘missing middle’.
Anemic growth and lack of employment opportunities are just some of the challenges this segment confronts as it fails to scale. Lack of access to finance and technical know-how, inadequate skills (both operational and technical), poor infrastructure facilities, high production costs and socio-economic constraints are just some of the challenges that MSMEs face in taking their businesses to the next level.
To compete globally, MSMEs need a nine-fold increase in digitally skilled workers by 2025. Such competencies include data analysis, cross-network collaboration, on-demand learning, and real-time response to operational change.
While the answer partly lies in providing MSMEs with easy, equitable access to credit to boost their manufacturing facilities, the right policies, a supportive ecosystem and pivoting on technology will be key to helping this sector grow.
Enabling Policies for the MSMEs Sector
The Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan was a response of the Indian government to counter the pandemic’s negative impact on the MSME sector. The MSME sector has been given a significant allocation and priority in implementing the measures that will revitalize the economy. Various announcements have been made under the package to aid the MSME sector immediately.
The Government of India, for example, has lately embraced a clustering and networking approach to assist MSMEs in improving their competitiveness during difficult times. The government is also working to address the needs of the various industries by offering various level courses through its training institutes distributed across the country.
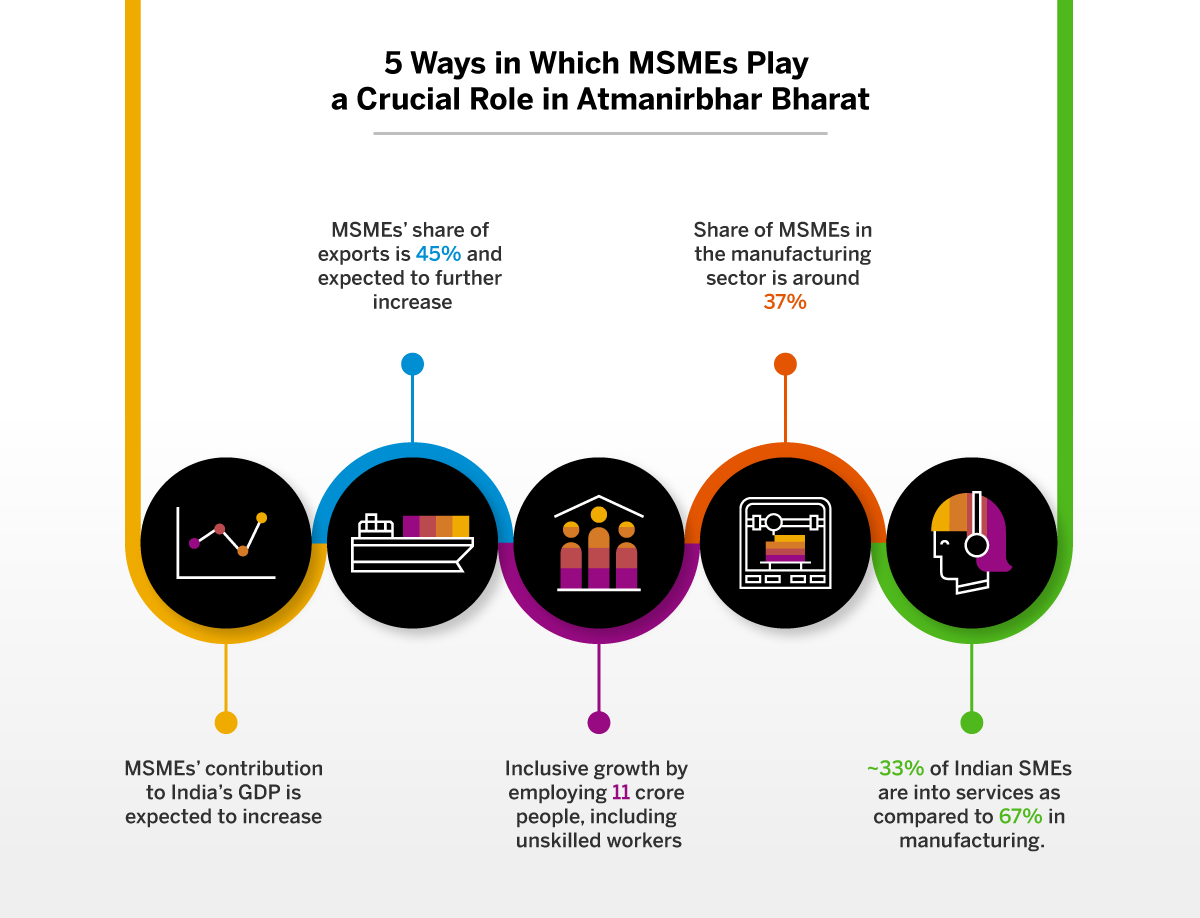
The reason for the government to stress on the importance of MSMEs can be understood by the contribution the MSMEs can provide to achieve the dream of Atmanirbhar Bharat. Here are the five main ways in which MSMEs are playing a crucial role in Atmanirbhar Bharat:
- MSMEs share in GDP- As per the report by India Brand Equity Foundation, the number of MSMEs in India has increased as a CAGR of 18.5% from 2019 to 2020. MSMEs’ contribution to Indian GDP is expected to increase in the future with the startup boom and formalization of the economy. The facilities like Government e-commerce Marketplace (GeM) are helping the small and mid-sized companies to grow further. As of June 25, 2021, the GeM portal has fulfilled 6.87 million orders worth $15.67 billion. One of the biggest hindrances for MSMEs has been their slow adoption of technology. But, with the government impetus, the technological adoption might increase, and the MSMEs might become more competitive.
- MSMEs’ share of exports- Exports are essential for any economy. The Indian economy has had a constant balance of trade deficit for many years. This balance of trade has been funded by remittances and foreign investments over the years. If India really wants to become self-reliant, the exports need to increase. The share of MSMEs in exports is 45%. The companies involved in exports are more profitable than the companies involved in serving the domestic market in India. Thus, exports are an essential part of the government’s mission of an Atmanirbhar Bharat. The government has introduced the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS). It is an incentive program to help the Indian companies become more competitive and to increase the export of goods manufactured or produced in India, in the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) for 2015-2020. MSMEs participating in exports are rewarded in duty credit scrips. Policy measures like these are expected to further increase the share of MSMEs in exports in the coming years.
- MSMEs’ growth is more inclusive- MSMEs in India employ around 11 crore people. The types of jobs created by MSMEs include unskilled workers as well. The MSMEs are known to create many jobs at a low capital cost. Thus, even a low capital can get inclusive growth. Inclusive growth is an important parameter of Atmanirbhar Bharat. As per the government data, 13% of registered MSMEs are providing 42% of the total jobs. Thus, there is a need to provide the required funds to MSMEs to help them grow as the growth will quickly trickle down into various jobs.

The United Nations commemorates 27th June as World MSME day. The United Nations understands the inclusive growth promoted by MSMEs and is taking various steps to help the MSMEs get back to business after the pandemic. They have recognized that the services sector is more impacted because of the pandemic, and they are putting their efforts into the services sector. The services sector is known to provide employment to temporary workers and to promote inclusivity. MSMEs are being helped by the Indian government and United Nations as well.
If India is to become a $5 Trillion economy by 2025, the share of MSME is expected to reach 50%. Thus, MSMEs will contribute to growth in the future. Also, informal employment in India is very high. With the formalization of the Indian economy and high growth in the MSME sector, inclusive growth can become a reality, with jobs being created even in the remote areas of India. If jobs are provided to remote areas, India can truly achieve the dream of an Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- MSMEs in the manufacturing sector- A key aspiration of being Self-Reliant is to make India a manufacturing powerhouse. This is envisioned by the Make in India policy of the government. As per government data, the share of MSMEs in manufacturing is around 37%.The contribution of MSMEs is expected to be huge if India is to increase its manufacturing output. Manufacturing requires a fast time to the market and changing the requirements as per emerging trends. Also, it requires a marketplace to sell the goods. With the growth of e-commerce and the Government e-commerce Marketplace (GeM), the selling opportunities are immense. Also, the emerging trends are easy to identify because of the easy availability of information. Indian manufacturing is showing signs of cyclical growth, and the contribution of MSMEs is immense. India has increased its ranking in Ease of Doing Business and is currently ranked 63rd. Schemes such as PLI schemes are expected to increase the manufacturing output of the country.
- MSMEs in the Services sector- India’s share of the services sector in the economy is 55%. Just as the manufacturing sector is essential, the services segment plays an important role as well in India’s economic growth. Most of the informal jobs exist in the services sector, and the services sector was the most affected because of the pandemic. As far as SMEs are concerned, around 33% of Indian SMEs are into services as compared to 67% in manufacturing.Most of the startups are also in the services sector. MSMEs have an important role to play in the services sector to provide employment to the gig workers, temporary workers, unskilled workers etc. If India is to be self-reliant, the importance of the services sector must be highlighted and the sector should be prioritized.
Technology can unlock the next phase of growth
Indian SMEs face significant obstacles in the globalization and liberalization period despite all significant efforts made by the government. The country can become Atmanirbhar if MSMEs can scale up to compete with global peers and participate in international market opportunities. It’s possible to make this a reality if MSMEs are more vigorous in adopting technology to get a competitive advantage.
Indian MSMEs are starting to integrate new and innovative information and communication technologies on a big scale, such as Software as a Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). MSMEs in India may hire external consultants or take other actions regularly.
Technology transfer, such as vertical technology transfer or horizontal technology transfer, is another option to be considered by the Indian MSMEs.
Despite the obvious benefits that technology can provide micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises, this segment has not been as aggressive in undertaking digital transformation. Digital proficiency is the need of the hour if this sector is to survive disruptions and build business resiliency. Digitally connected MSMEs can get better access to the market and take advantage of a borderless marketplace.
For MSMEs to compete globally, programs such as SAP’s Global Bharat initiative can be of great help. Besides enabling digital skilling for the workforce, this program also provides access to B2B marketplace. Growing businesses need to have an enterprise resource planning (ERP) system in place since it helps bring in efficiency and enhance productivity. From automating routine business processes to reducing human intervention to integrating key business processes, ERP is extremely beneficial to MSMEs.
Some of the benefits of having an ERP system include the ability to minimize errors due to automation, see real-time inventory and gain insight from well-structured data. A cloud-based ERP provides flexibility and real-time analytics. Having real-time analytics can help faster decision-making based on up-to-date, real-time information. As an MSME, having access to real-time information will help the decision-making process while optimizing resources and costs.
MSMEs are beginning to realize the advantages provided by ERP systems. India is adopting ERP solutions at a faster clip than the rest of the Asia Pacific region. According to a NASSCOM study, SMEs can contribute up to 30% of the cloud market. The study showed that 60% of the SMEs are already using cloud, although half are at the early stage of adoption. Of course, adopting cloud has helped SMBs reduce operational costs while increasing productivity.
Change is inevitable, but if MSMEs are geared to deal with change, then it becomes easier to cope with challenges that arise. RISE with SAP brings together offerings that can help transform business strategically. From being able to stay agile to bringing in efficiency that lets MSMEs stay in control of their business, this initiative is specially designed for MSMEs.
Staying connected to business owners going through the same challenges offers unparalleled opportunities to learn from industry peers. Stay in touch with over 15000 business owners to learn how they rise above challenges and stay innovative. From engaging with the MSME community to learning about the latest technologies, the Growth Matters Forum, a vibrant online community, provides insights and helps keep track of the upcoming trends and growth opportunities in the MSME business.



