The Internet of Things (IoT) has firmly entrenched itself in the retail sector. From Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags and sensors to beacons and cloud, connected devices are busy helping retailers personalize and enhance shopping experiences for today’s connected customers. Through robust and continuous data exchange, IoT retail software creates a real-time network of information sharing between different components of the retail value chain. It has also led to the seamless omnichannel shopping experience that all consumers have come to expect.
As consumers step outdoors, omnichannel will continue to hold sway. Nearly 70 percent of consumers are expected to research both in-store and online before making a buying decision, says the latest McKinsey survey. What is of particular interest from this survey on U.S. consumers is the expectation that both e-commerce and brick-and-mortar business will continue to grow. Hence, implementing IoT retail software becomes increasingly important for traditional retailers as they are compelled to change their business model for in-store operations.

Consider this: large retail chains such as Macy’s, American Apparel and Marks and Spencer have adopted RFID tags in their stores, while John Lewis and Tesco have launched apps that allow a customer to make payments from anywhere in the store, and not necessarily at the checkout counter. Avery Dennison uses IoT sensors to track up to 10 billion items at a time; Kroger is deploying such sensors to track and monitor cargo containers. Walmart has introduced robotics for better customer service. The list is long and ever-growing!
Reimagining the customer experience
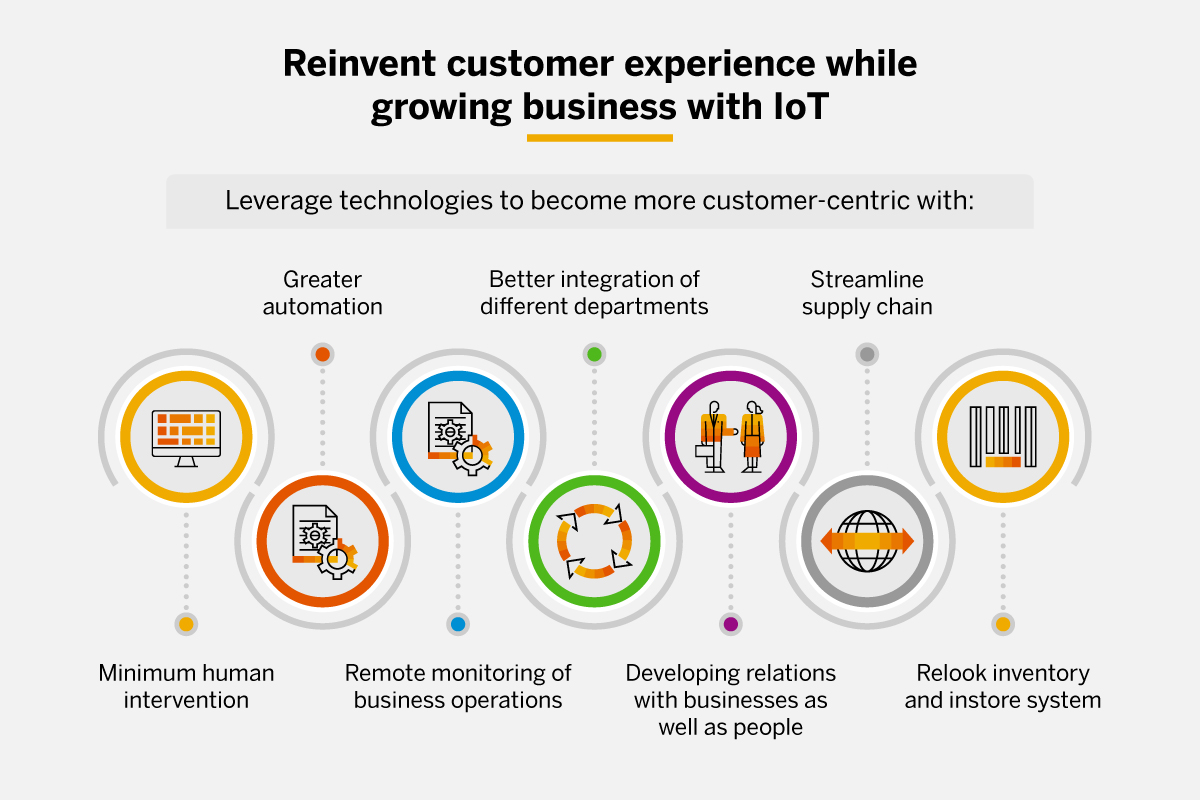
Consumer expectations and buying habits have changed, and they are here to stay, as is reflected in a recent Accenture study. For retailers, this means an excellent opportunity to leverage technologies such as IoT to become more customer-centric. It also provides unprecedented opportunities to harness data from these connected devices to reinvent customer experience while growing their business in an informed way. So how does IoT enable this? This is possible due to
- Minimum human intervention
- Greater automation
- Remote monitoring of business operations
- Better integration of different departments
- Developing relations with businesses as well as people
IoT systems and devices, such as RFID tags, help improve store operations and augment sales. Breaking it down further, IoT can help retailers:
- Streamline their supply chain
- Enhance customer experience
- Relook inventory and instore system
Doubling down on elevating customer experience and customer service
One of the key learnings of the pandemic is for retailers to move away from the store and product-centric sales metrics and focus on shifting customer behavior. This will help design customer-centric strategies ranging from marketing to in-store experience. With IoT-powered retail POS software, retailers can analyze data to recreate the buyer’s persona, based on demographics and purchase history. Creating a personalized customer journey can drive the consumption of goods and services. Some use cases include:
- Harnessing data to create personalized customer interactions could include time spent by a customer at a kiosk and whether they made comparisons between brands. This can help design the marketing campaigns, as well as assist in analyzing the success or failure of existing campaigns. Quite helpful actually, if you consider that 40% of consumers will continue to switch brands and that this number is even higher for the younger and high-income consumers, as found by McKinsey.

- Recommending optimized product usage, based on consumer preferences. When retailers adopt such practices, it will enable them to make strategic decisions about stock placement and replenishment, based on customer interaction with products displayed on the store shelves.
- Reducing wait times by optimizing last-mile delivery. Increasingly, IoT is being used for more complex purposes, such as ‘last mile’ solutions like self-driving cars and drones for delivery trips between retail stores and consumer homes. For example, Ericsson, Einride, and Telia have teamed up to create self-driving vehicles at a logistics firm’s plant in Sweden using 5G-powered IoT. Even Ford and Amazon are conducting deliveries with self-driving cars and drones.
Better customer experience is also being delivered through protocols such as the IoT Gateway. The IoT Gateway comprises software components that directly interact with devices. Together, they bridge the communication gap between devices, sensors, equipment, systems, and the cloud. For retailers, this allows them a never-before opportunity to know their customer better while analyzing important but often ignored data points (Think: the amount of time customer spends in the wait line to the walking route within a shopping mall to reach the brand’s outlet).
Besides delivering a better shopping experience to consumers at home, IoT-enabled retail software has also enabled smart and unstaffed retail stores where the human element is absent. Instead, all services are performed through connected technology. For the customer, this novel in-store experience only requires a smartphone.
Since the opening of the first such store in Sweden in 2016, many unstaffed retail shops have come up. Big companies such as Alibaba and Amazon have already launched such stores. Alibaba, in partnership with Ford, even has a ‘vehicle vending’ smart machine. The unmanned facility lets customers virtually ‘browse’ the cars stored in a vending machine, via their smartphones. Customers can then make their purchase and have the vehicle delivered at ground level.
Singapore-based telecommunication company Singtel’s unmanned retail store, named Unboxed, has taken the telecommunications scene in Singapore by storm. Powered by facial recognition technology, Unboxed allows customers to consult with a roving live bot. The bot can provide personalized recommendations, phone tryouts, and mobile plan registrations at video-assisted self-serve kiosks. It also enabled the customers to collect purchases on the spot, and browse and buy accessories such as headphones, phone cases, power banks, and handsets.
Unboxed also allows customers to pay bills, top up prepaid cards and Dash wallets, and get SIM card replacements without the physical presence of company personnel. Using 5G internet, the hyper-connected store offers an unmatched consumer experience. Apart from a reliable network to support a hassle-free shopping experience, the IoT technology used in the store makes transactions easy and convenient.
Smarter inventory management for strategic decisions
One of the most popular applications of IoT-based retail software is smarter inventory management, where sensors and devices help retailers streamline inventory and be more strategic in replenishing stocks. IoT technology in both inventory and warehouse can increase visibility into production, inventory management and supply chain.
Take the case of a retailer who is seeking to enhance customer experience by ensuring products browsed online are available in the store, or that customers get access to the right product (of a particular make, model, price, size, etc.) in the right quantity at the right time. For this to happen, there needs to be a tight integration of inventory and supply chain. Solutions such as Smart Shelf Technology help streamline inventory by using real-time data analysis to provide notifications about when to restock items and providing alerts about faults and errors in the system. There are dual benefits of such alignment:
- Matching fast-moving supply with the requisite demand
- Keeping up with omnichannel retail strategies such as the ‘Buy Online, Pick Up in Store’ (BOPS). BOPS requires a highly efficient inventory management system, as well as a time-critical delivery and notification system.
Warehouse management systems – Warehouses and other storage spaces can also be managed efficiently with the help of IoT tools like warehouse management systems. IoT allows managing high-volume warehouse operations through applications such as on-premise and cloud deployment, completely integrated quality, production, track-and-trace procedures, and direct control of warehouse automation equipment. By integrating complex supply chain logistics with warehouse and distribution processes, IoT-based technology allows for the management of inventories remotely and in real time. These systems provide the users with features such as:
- Advanced shipment notification
- Maintenance, replenishment, slotting and rearrangement of inventory
- Transportation wave management
- Packing control and process monitoring
End-to-end supply chain visibility to counter disruptions
One of the most noticeable side effects of the global health crisis was supply chain disruption, which did not spare the retail sector either. And latest news reports state supply chain woes will get worse before it gets better. Retailers with global supply chains are likely to fare a lot worse, but here’s where technologies such as IoT kick in. By its very nature, IoT enables end-to-end visibility throughout the entire supply chain from source at origin to delivery at destination through real-time monitoring and tracking. Let’s look at how IoT in the supply chain plays out:
- Predictive maintenance– Through supply chain and logistics management solutions, data from sensors such as pressure and temperature sensors can be used to pre-empt any problems with a cargo. This helps to:
- Get a real-time, 360-degree view into the supply chain
- Target and eliminate potential bottlenecks
- Mitigate other risks with on-premise and cloud logistics management systems.2. Transportation planning-Provides real-time visibility into transportation resources so that customer demands can be met at minimal cost. This is done through:
- Tracking and monitoring transportation resources
- Forecasting supply and demand using advanced computation models
- Improving transportation resource planning by stimulating scenarios to correct and prevent imbalances
- Optimizing empty resource movement by finding the optimal locations and dates for the pick-up and return of transportation resources
- Creating event-triggered alerts to provide timely warnings
3. Yard Management systems-These help the retailers run more efficient and profitable supply chain logistics with a range of visualization and reporting tools. With this software, retailers can:
- Efficiently plan orders and appointments, integrate and automate resource use and incoming and outgoing transport.
- Speed up yard execution and processing, helping faster deliveries of products and services along with improved service and enhanced visibility and control.
- Identify, avoid, and solve potential issues through comprehensive graphical monitoring.
- Through accelerated gate-in and gate-out processes, efficient use of assets and areas, and increased productivity of existing equipment, the program enables retailers to achieve a significant reduction in processing time. Reduction in staffing needs also allows for faster execution of activities and increasing yard throughput.
CONCLUSION
Without a doubt, the use cases and applications for IoT-powered retail software will only continue to grow, and the possibilities are limitless. While the trend of unmanned retail stores is yet to catch on, achieving a completely human intervention-free retail world does not seem so far-fetched now. Fully-automated supermarkets are now visible in different parts of the world, with RFID tags, intelligent kiosks, virtual tables, AR applications and many more examples of in-store technologies. Other IoT features, such as predictive engines and SSD algorithms, can also help in enhancing the efficiency of such automated retail systems.
The adoption of ‘smart’ technologies is leading to happier consumers, as ease of use brought about by IoT-based devices significantly increases perceived usefulness and perceived enjoyment of the product. This also positively affects shopping intention.
As the retail sector gets more crowded, data-centric retailers are undoubtedly poised for success. Yet, the inherent technological challenges need to be tackled with the help of an experienced partner. SAP helps businesses maintain efficient and cost-effective systems for businesses. With solutions focused on transportation resource planning, logistics and warehouse management, among many others, SAP helps retailers leverage the power of IoT-enabled retail software and position themselves firmly on the cutting-edge of this trend.



