In an increasingly complex world, partnering across industries and sectors to achieve shared sustainability goals has become an imperative. The enormity of our modern day challenges — including reaching net-zero emissions and significantly reducing plastic and other waste — means that we need to develop entirely new value chains. No business can do that on its own.
Businesses and organizations need to act together, leveraging collective networks, influence, and expertise, in order to bring real transformation and generate positive outcomes.
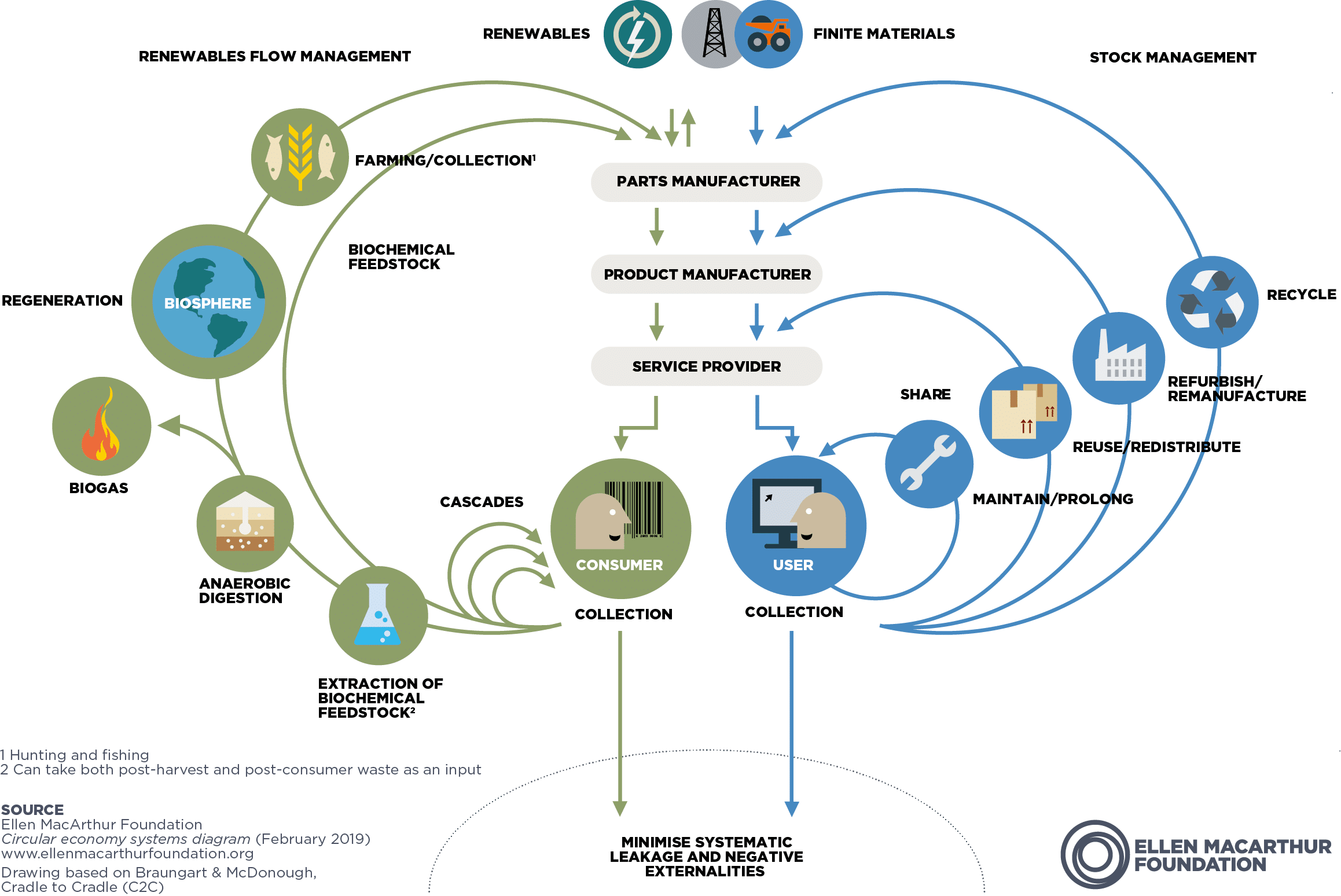
SAP has become a partner in the Ellen MacArthur Foundation’s network to deliver circular economy solutions led by regenerative business with customers, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and partners.
The partnership formalizes the organizations’ joint commitment to accelerating the transition to a circular economy based on three key principles: eliminate waste and pollution, circulate products and materials, and regenerate nature through innovative business models and systems-level change.
Andrew Morlet, CEO at the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, said: “We are pleased to welcome SAP as a partner. Collaboration across all sectors and industries is critical in order to shift the system and accelerate the global transition to a circular economy — an economy designed to eliminate waste and pollution, circulate products and materials, and regenerate nature. Technology has a crucial enabling role to play, and we welcome SAP’s leadership in this space.”
The partnership will focus on three key pillars:
- Powering circular design
- Actioning extended producer responsibility
- Enabling regenerative business via digital solutions
One of the key elements of a circular economy is design, including product design, policy design, and systems-level design. According to the Foundation, there are over 160 million designers in the world; connecting with them is crucial to solving the world’s waste problem. Technology will play a key role in enabling that, equipping them with insights and data to make better material choices, as well as creating better transparency around ecosystems.
With only nine percent of the 400 million tons of plastic produced every year recycled, plastics is an issue where the urgent need to act is being recognized at the highest levels of global policy-making. United Nations (UN) member states recently agreed to adopt a legally binding multilateral treaty on plastic pollution, the text of which explicitly underlines the importance of promoting the circular design of products and materials. According to Inger Andersen, executive director of the UN Environment Programme, the agreement is the “most important international multilateral environmental deal since [the] Paris [climate accord].”
Without collective and meaningful action, ocean plastic is expected to nearly triple from 11 million tons in 2016 to 29 million tons in 2040, wreaking havoc on fragile marine ecosystems. This dire situation is a clarion call to act on extended producer responsibility (EPR), a policy framework that shifts financial responsibility from governments onto product producers for the management, treatment, and disposal of consumer products. This creates incentives for manufacturers to develop products that are more recyclable and less resource-intensive, in effect preventing waste at the source.
SAP has supported calls for EPR regulations, as have key customers that recognize such approaches can create competitive markets for recycled plastics and create a level playing field for companies that rely on plastic products.
Technology is undoubtedly needed to make EPR actionable in business. The partnership will see SAP bring its insights and innovation around digital solutions to enable the circular economy for a regenerative future, based on a non-extractive and replenishing principle, where businesses seek to give back more to society and the planet than what they take.
SAP launched its first major circular economy solution at COP26: SAP Responsible Design and Production, which provides the foundation for the company’s regenerative business mission and establishes a consistent measurement of material use globally. It helps companies gain better visibility of material flows through their business processes, manage EPR regulations worldwide, prepare for upcoming plastic taxes, and optimize material choices.
To further deliver transparency across the supply chain, climate solution SAP Product Footprint Management enables businesses to calculate product footprints across the entire product life cycle, providing actionable insights into the environmental impact of their products at scale and allowing companies to move toward lower carbon emissions.
Holistic sustainability performance management solution SAP Sustainability Control Tower enables companies to prioritize sustainable business results by providing insights for executive-level decision-making to manage and report financial and non-financial impacts of business processes.
Finally, SAP has recently launched a new cloud offering to help companies holistically measure, manage, and optimize their sustainability performance: SAP Cloud for Sustainable Enterprises.
With more than 50 years of managing resources across enterprise functions, integrating data into business processes, and networking businesses and industries around the world, SAP is uniquely positioned to build solutions to help companies run sustainably.
As Stephen Jamieson, global head of Circular Economy Solutions at SAP, puts it, “This partnership is based on our mutual ambition to deliver a circular economy led by regenerative business. We aim to achieve this by working collaboratively to solve critical design challenges with innovative solutions, and focusing on extended producer responsibility, the single most important policy intervention that will deliver the level playing field that’s required for a circular economy. Together we’re committed to innovating and delivering the solutions that make that policy intervention simple, consumable, and actionable.”



